We hear a lot about the imaging tests, but do you know what they look like? And what are these imaging tests actually testing for? Here is a list of imaging tests for the NCLEX.

- X-ray
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI
- MRA
- PET scan
What is the difference between all these!?
In nursing school, you didn’t get instructions on how to read an imaging test. And I’ve never seen an NCLEX question that shows an image and then you have to figure out how to read it. However, you do get NCLEX questions about how to care for a client before and after an imaging test. Also, you can get a question about what type of test the HCP might order. As the nurse, you’ll want to look up your client’s diagnostic tests to see what the results were.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the main imaging tests, what they look like, and what they are for.
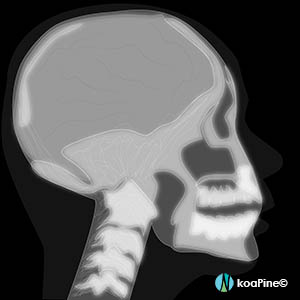
1. X-ray
X-rays are best for finding broken bones, tumors, dental decay, and the presence of foreign bodies.
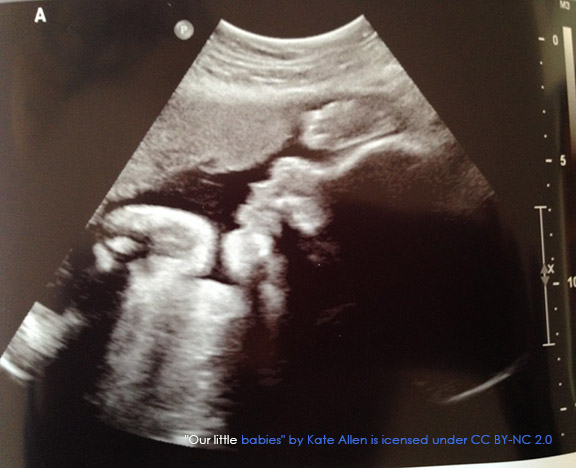
2. Ultrasound
Ultrasounds create images of soft tissue structures. They are best for seeing a developing fetus, a client’s abdominal and pelvic organs, muscles and tendons, or heart and blood vessels. They are very easy and safe to perform.
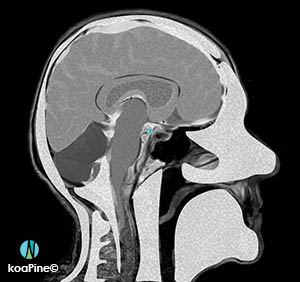
3. CT scan – computed tomography scan
CT scans can detect bone and joint problems, like complex bone fractures and tumors. They can also help to spot changes with cancer, heart disease, emphysema, or liver masses. They show internal injuries and bleeding, such as those caused by a car accident or stroke.
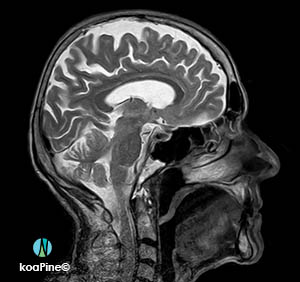
4. MRI – magnetic resonance imaging
An MRI can make detailed pictures of the inside of your body more than a CT scan can. It may be used to help diagnose or monitor the treatment for a variety of conditions within the chest, abdomen, and pelvis.
MRIs of the brain can be used to detect brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, developmental anomalies, multiple sclerosis, stroke, dementia, infection, and the causes of a headache.
5. MRA – magnetic resonance angiography
An MRA can make multiple images of blood vessels (arteries) using magnetic fields. MRA is used to generate images of arteries in the brain, chest, and abdomen in order to evaluate them for stenosis, occlusions, aneurysms or other abnormalities.
6. PET scan – positron emission tomography
A PET scan makes multiple images of a part of the body that uses a special dye with radioactive tracers that the client swallows, inhales or gets injected into the arm depending on the area of the body.
It can show abnormalities at the cellular level such as cancer.
PET scans are most often used to detect cancer, heart problems (such as coronary artery disease and damage to the heart after a heart attack), brain disorders (including brain tumors, memory disorders, and seizures), and other central nervous system disorders
Like how I explain things and the images that go along with it? Then, you’ll love my tutoring, webinars and flashcards!
Leave a Reply