Case study NGN NCLEX questions are a common type of NCLEX question. Case studies include all parts of the nursing process (AKA clinical judgement model) and are a great way to test your nursing knowledge.

The main things to know about a case study question are:
- each case study includes 6 questions
- students are getting about 5 case studies on their NCLEX (but only 3 count towards passing)
- students are reporting that they don’t seem super hard
A case study will start off by giving some nurses’ notes, vital signs and lab data. You’re job is to figure out the medical problem.
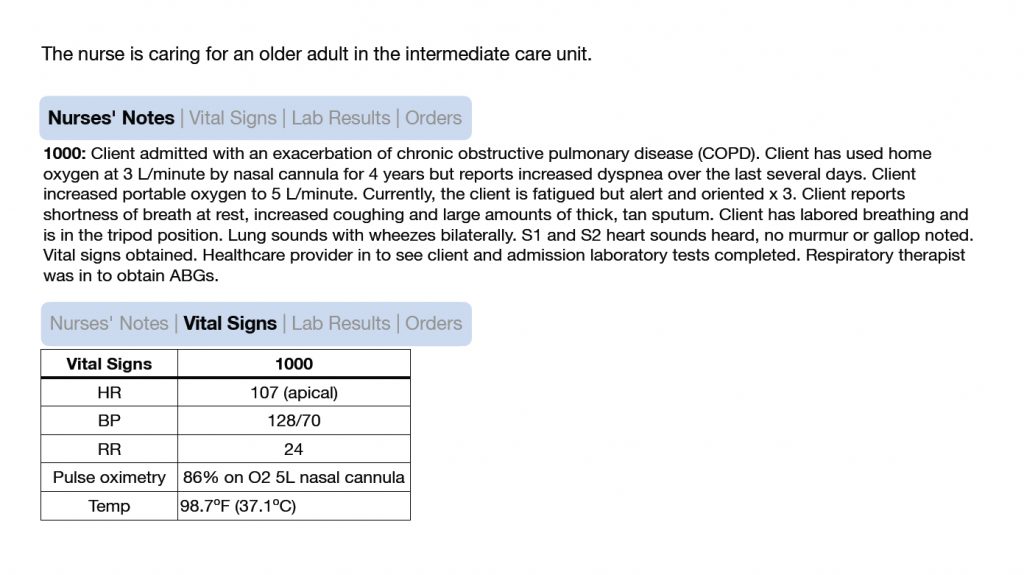
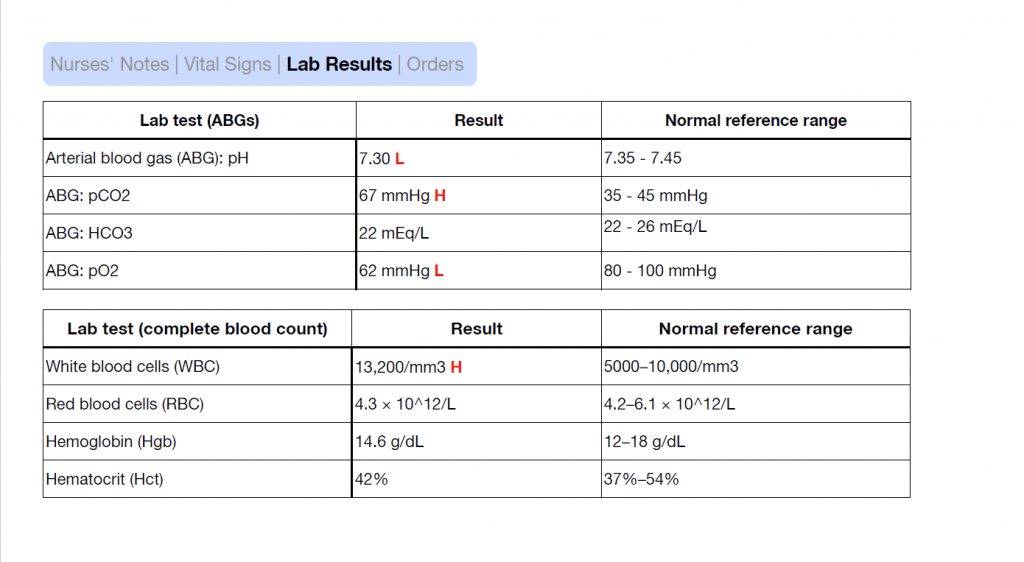
After going through the assessment data, what do you think is wrong with this patient?
That’s right! They are having a COPD exacerbation. They also might be developing an infection based on the “large amounts of thick, tan sputum” and the elevated WBC count. Based on the ABG’s do you know what acid-base imbalance they have? Yes, they have respiratory acidosis.
Question 1

You basically want to choose the labs and assessment data that supports the medical problem that the client has. Answers 1, 2, 4 and 5 are the abnormal lab values and support the problem of the COPD exacerbation and possible infection that is brewing. The answers are…

Question 2
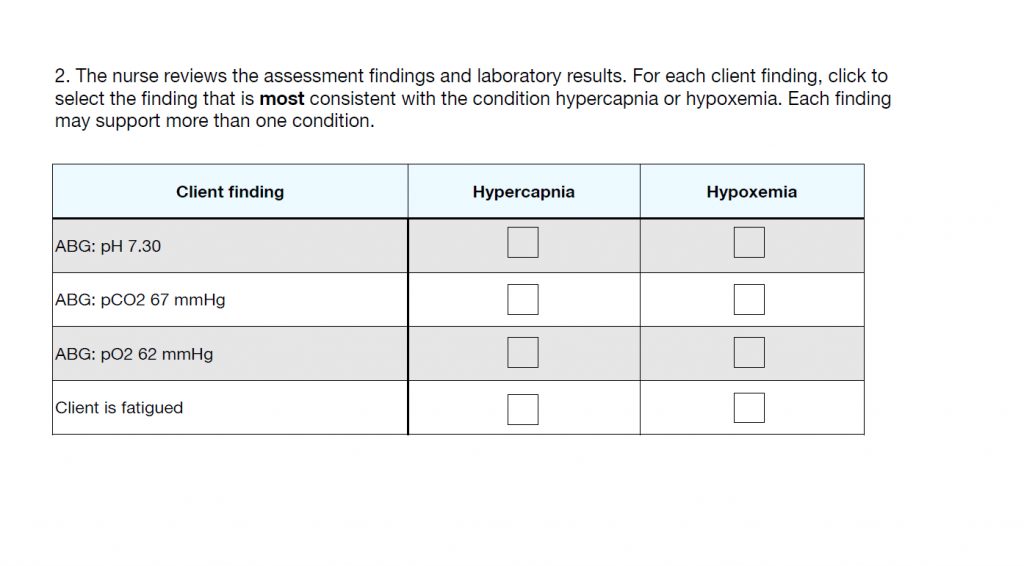
This question is about choosing the assessment findings that match up with either hypercapnia (high CO2 level) or hypoxemia (low oxygen level) or BOTH.
- A pH of 7.30 is acidic. With acidic blood, you will see a high CO2 since that also indicates acidity. You wouldn’t necessary see hypoxemia with hypercapnia, so don’t pick it.
- A high CO2 means hypercapnia, so choose that.
- A low O2 mean hypoxemia, so choose that.
- Fatigue can occur with a low O2 because not getting enough oxygen over a long period of time makes a person tired, since you need oxygen to function. Also a high CO2 level can cause fatigue, since that is a toxin, which the body doesn’t like and can make them feel tired and sick. The answers are…
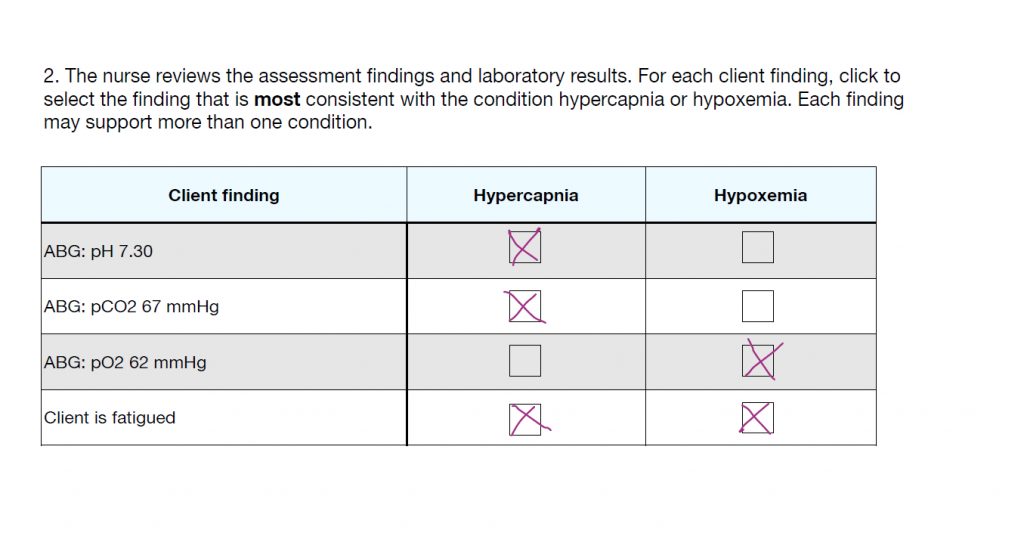
Question 3
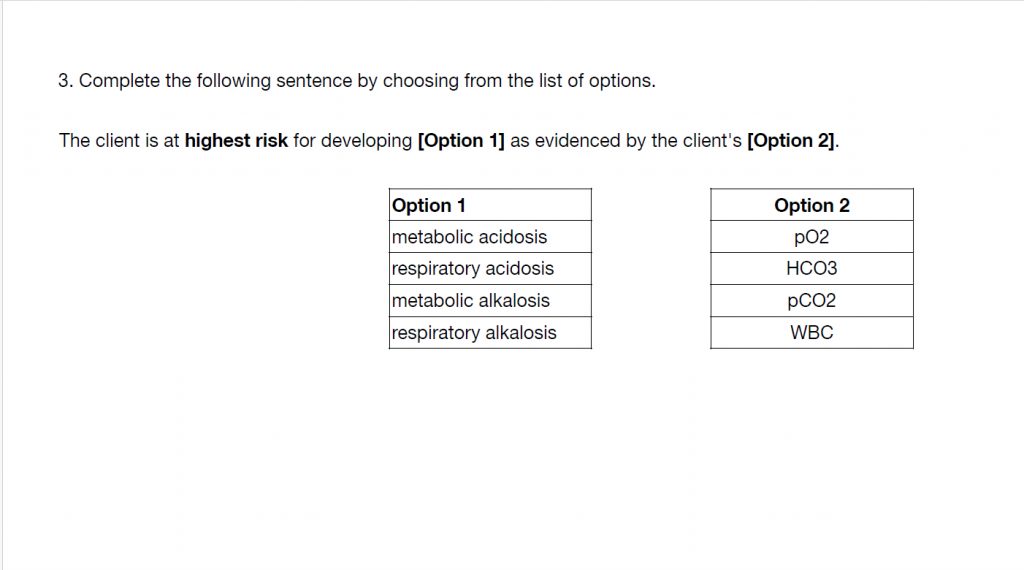
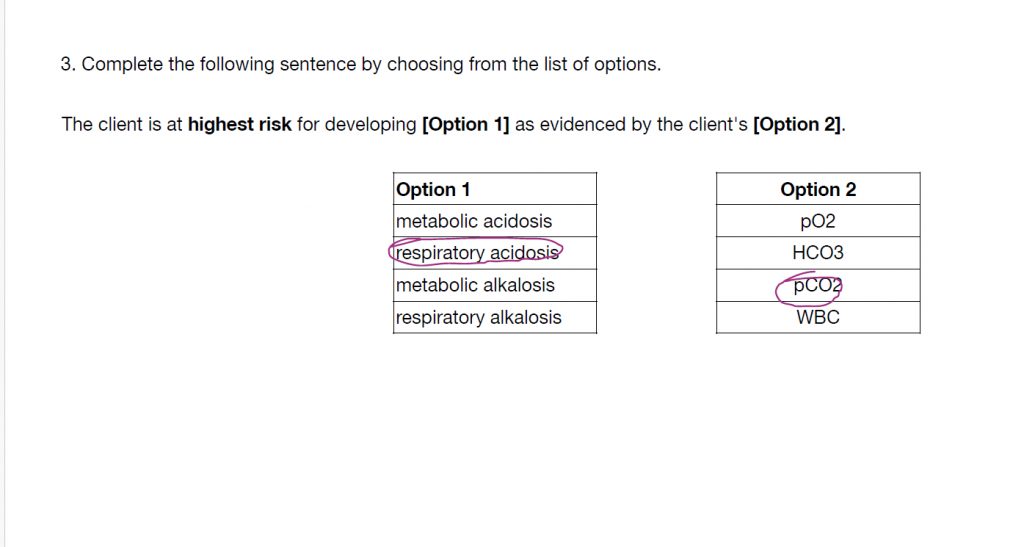
With question #3, you have to figure which acid-base imbalance this client is most likely having. All you have to do is interpret the labs. The pH is acidic. The CO2 is acidic and the HCO3 was normal. This client has Respiratory Acidosis. Which lab tells you this? That’s right, the CO2, since it is high, making the blood acidic. The answers are..
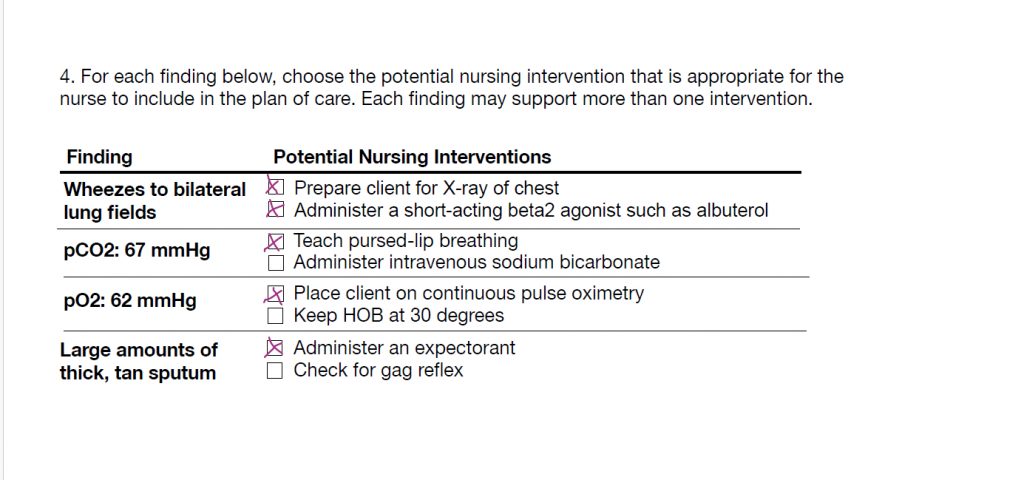
Question 4

Now that you know the client is having a COPD exacerbation, is in respiratory acidosis and has an infection brewing, it’s time to do something! Do some ongoing assessments and some interventions.
For each of the categories above, you have to choose at least one answer.
A) Wheezes to bilateral lung fields:
- Do both an x-ray of the chest and give albuterol. The x-ray will give us more assessment data to see how bad the client’s lungs are. Giving albuterol will help open up the airway so the client can breathe better.
B) CO2 of 67:
- Pursed lip breathing will help the client blow out the extra CO2 level. But giving sodium bicarbonate really only works to neutralize the acid for a client with metabolic acidosis, not respiratory acidosis.
C) O2 of 62:
- Place the client on continuous pulse oximetry to help gauge how well the client is doing or not doing.
- Keeping the client’s head of bed at 30 degrees is not high enough. Remember that in the notes the client was in the tripod position which is leaning over. Putting them at 30 degrees prevents the lungs from being able to open up fully. Put the client higher such as 90 degrees (sitting straight up).
D) Large amounts of thick, tan sputum:
- Give an expectorant. This is a med that helps get gunk out of the lungs. But checking for a gag reflex is a do nothing answer. It doesn’t help with breathing or getting the mucus out.
The answers are…
Question 5
As you can see below, you have some orders now. Then the question asks about the 3 teaching points in regards to the medications.

You should know what the meds are for.
- Albuterol: bronchodilator to open up the airways
- Fluticasone: steroid to decrease inflammation
- Guaifenesin: an expectorant to get the gunk out of the lungs by coughing
If you now what the meds are for, it’s a lot easier to choose answers.
- #1 is not the answer because it’s guaifenesin that helps remove excessive thick secretions, not albuterol
- #2 is not the answer because it written in the wrong order: bronchodilator first, then steroid
- #3 is an answer because albuterol has a side effect of tachycardia and nervousness
- #4 is not an answer because you have to rinse the mouth after a steroid since it can cause thrush
- #5 is definitley an answer since this is about safety
- #6 is also an answer since breathing out slowly will help keep the medication in the lungs for longer
- The answers are…

Question 6
The last question is usually an evaluation type of question. This is when you have to decide if the patient got better or worse. I just keep it as a simple GOOD/BAD. What’s good? What’s bad?
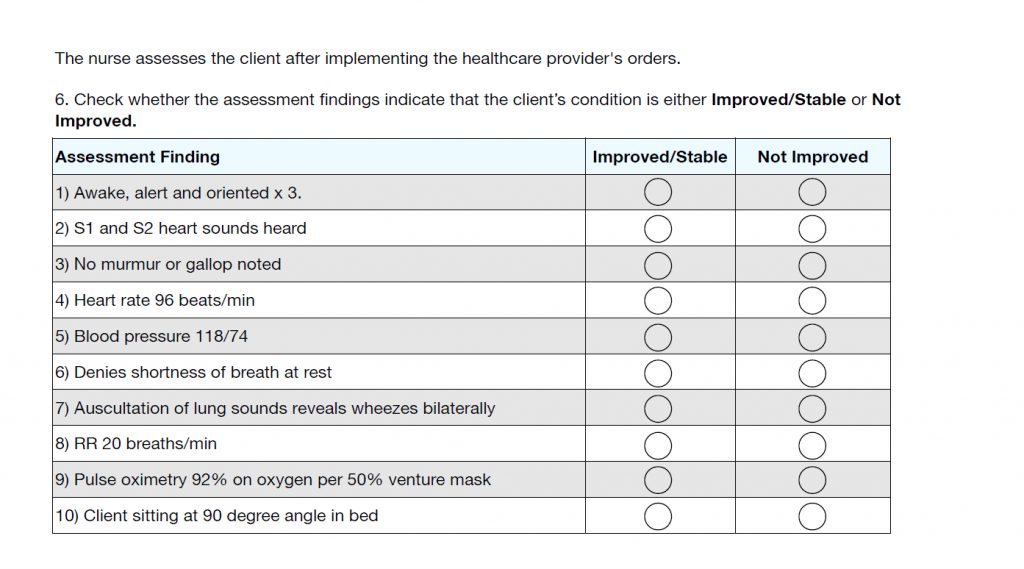
All the answers are Improved/Stable or “good” except #7. If they still have wheezes, then they have not improved. Answers are…
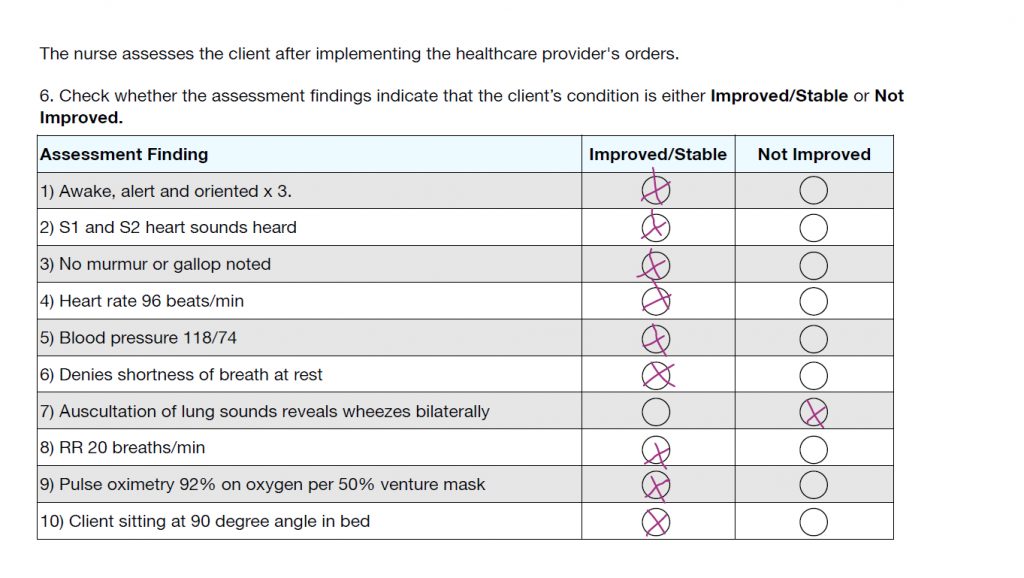
As you can see this client had a medical problem of COPD exacerbation with a possible infection. Always keep the medical problem in mind, and then go back to the notes/tabs if you need to review the information.
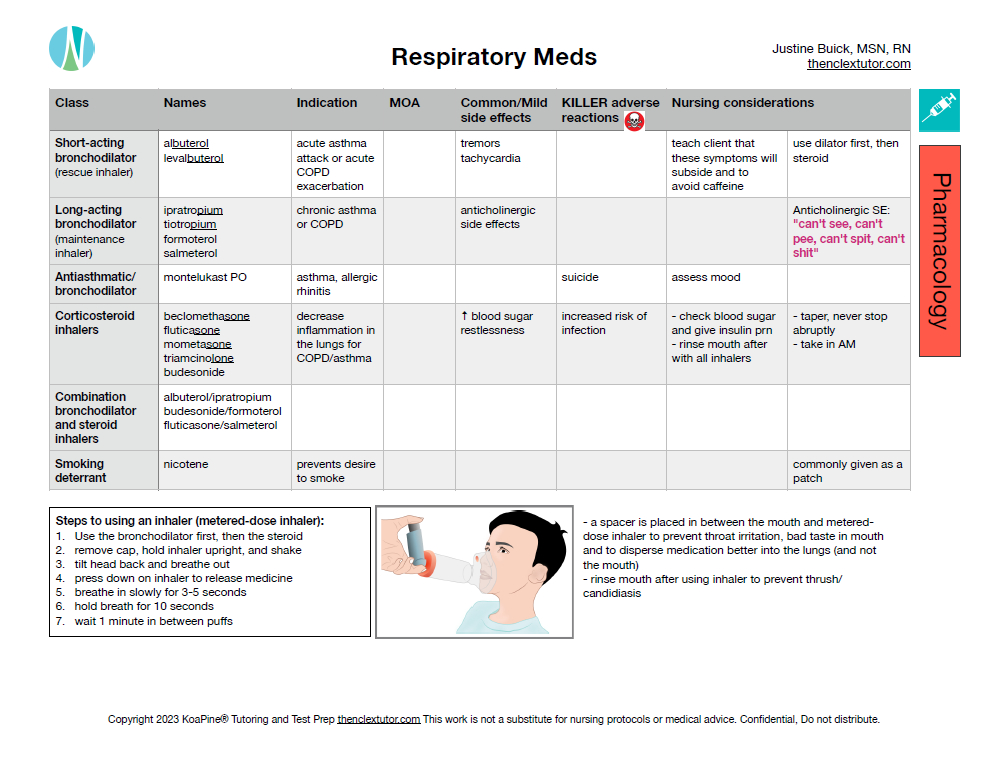
If you had trouble with content, then you can check out my nugget pages book. Below is an example of the respiratory meds section.
If you are interested in tutoring, go to thenclextutor.com/contact and fill out the form.
I hope you found this helpful!
VERY HELPFUL PRACTS QUESTIONS