I had a nurse with over 30 years of cardiac experience teach me about EKGs and how to read them. She worked in the ICU and was part of the Rapid Response Team.
I immediately loved this person’s style of teaching because she simplified everything so that we could understand. She was a teacher at heart. It was a life changing moment because I no longer dreaded taking care of a client on a heart monitor! Cardiac EKGs on the NCLEX is a big topic. And cardiac disease is a big problem. Reading an EKG is a fundamental skill every nursing student should develop before they take the NCLEX.

There is a lot to know about EKGs and even “simplified EKG” books, videos and other blog posts can be a bit overwhelming. So this is my simple, SIMPLE version of what to know about EKGs.
There are 2 main things to know about Cardiac EKGs on the NCLEX.
- Can you recognize what the rhythm is?
- Do you know what meds to give and other basic interventions if the client is having symptoms?
1) Normal sinus rhythm – 70 beats per minute
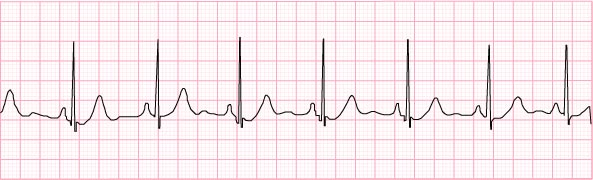
- No interventions
2) Sinus bradycardia – 40 beats per minute
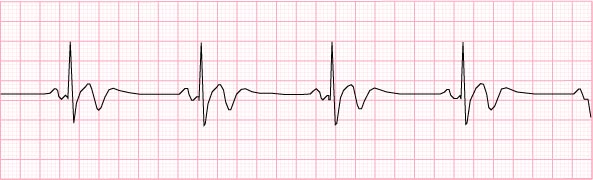
- no interventions unless showing symptoms
- give atropine or client gets a pacemaker
- it will speed the heart rate up
3) Sinus tachycardia – 130 beats per minute
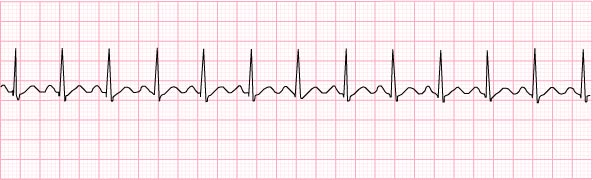
- give meds to slow the heart rate down
- beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, digoxin
4) Asystole – 0 beats per minute
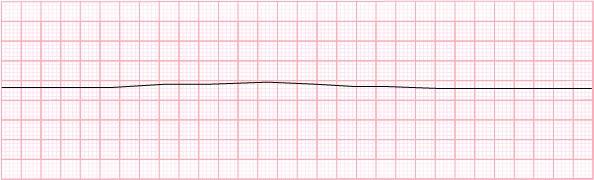
- start CPR
- epinephrine
- NO DEFIBRILLATION
5) Ventricular fibrillation – no obvious heart rate
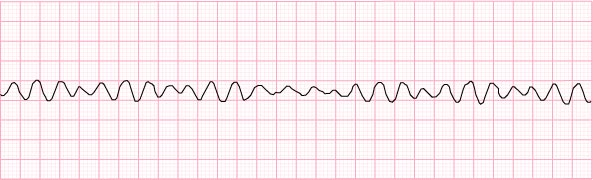
- CPR
- defibrillation
- epinephrine
- amiodarone (give lidocaine as an alternative)
6) Ventricular tachycardia – may or may not have a pulse
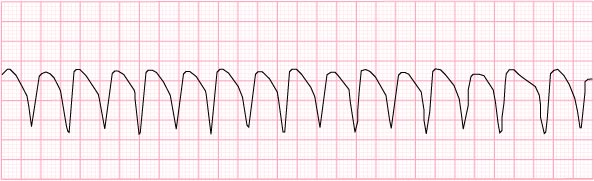
- Pulseless
- CPR
- defibrillation
- epinephrine
- amiodarone (lidocaine as an alternative)
- With a pulse
- amiodarone (lidocaine as an alternative)
7) Myocardial infarction – ST segment elevation
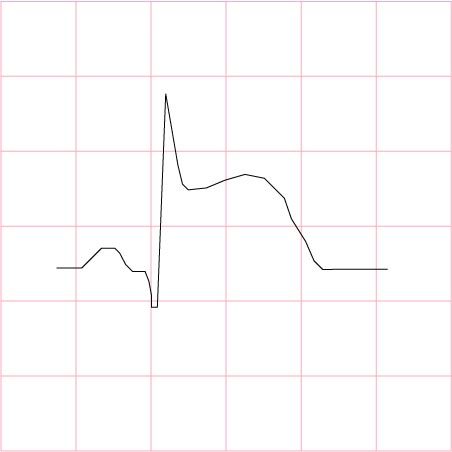
- OANM
- oxygen
- aspirin
- nitroglycerin
- morphine
- thrombolytics within the first 6 hours if from a clot
- T-PA, retepase
8) Atrial fibrillation – 90 beats per minute and irregular
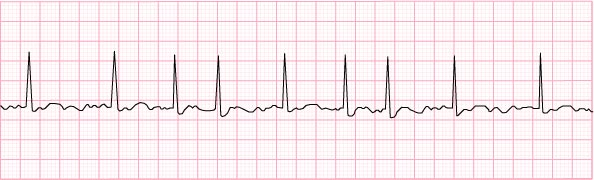
- high risk for blood clots
- anticoagulants
- antiplatelets
- meds to decrease heart rate
- beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, digoxin
9) Atrial flutter – 70 beats per minute
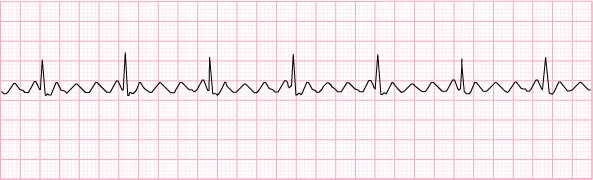
- same care as atrial fibrillation – see above!
Heart Blocks
10) 1st degree AV block – 70 beats per minute
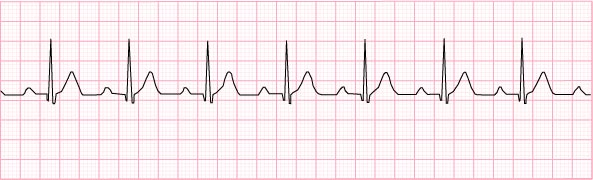
11) 2nd degree AV block Type 1 (Wenkebach or Mobitz I) – 50 beats per minute and irregular
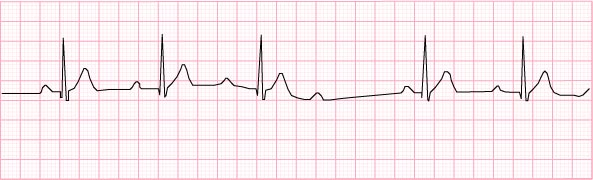
12) 2nd degree AV block Type II (Mobitz II) – 60 beats per minute and irregular
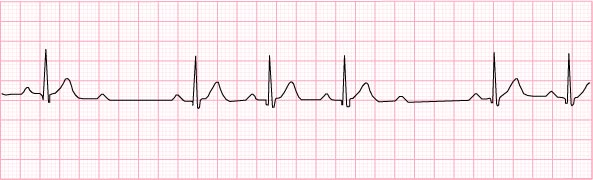
13) 3rd degree AV block – 30 beats per minute
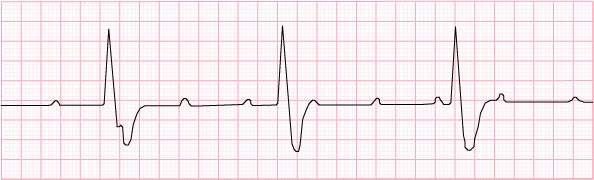
- General treatment for all heart blocks
- give atropine or client gets a pacemaker
- it will speed the heart rate up
14) Superventricular tachycardia – 170 beats per minute
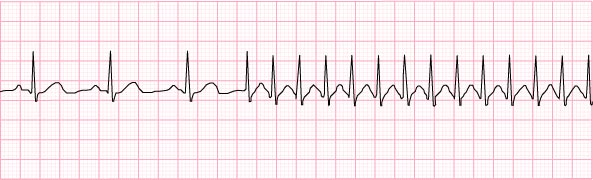
- give adenosine: will convert to normal sinus rhythm
15) Pre-ventricular contractions – 110 beats per minute and irregular
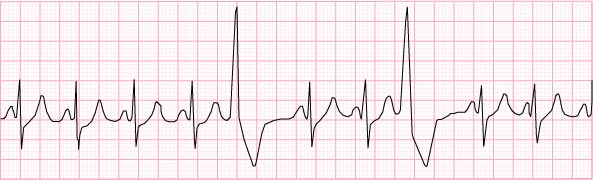
- give meds to slow the heart down and prevent the PVCs
- beta blockers, amiodarone, flecainade
16) Torsades de Pointes – no obvious pulse
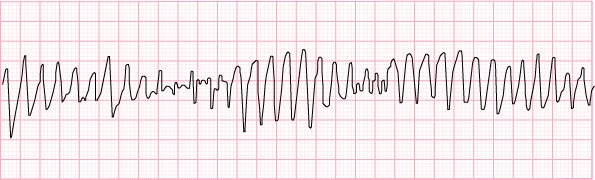
- give IV magnesium first
Like I mentioned in the beginning of this post, Cardiac EKGs on the NCLEX are a big topic. Get prepared so you can feel confident answering these types of questions!
Good
Wow, this was soo helpful. Thanks for simplifying my worse topic! 🙃
This is great!
THANK YOU!
Thanks. This ECG simplified